The causes of oral mucosal infections or inflammation in the oral cavity are varied. Most often, infections with viruses, bacteria, or fungi are the underlying cause. Mechanical irritants such as pressure sores from dentures or sharp tooth edges can also be triggers. Furthermore, allergies—for example, to certain toothpastes or filling materials—play a role, as do underlying systemic diseases (e.g., diabetes or iron deficiency). Risk factors such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption further promote the development of these conditions.
These symptoms occur frequently
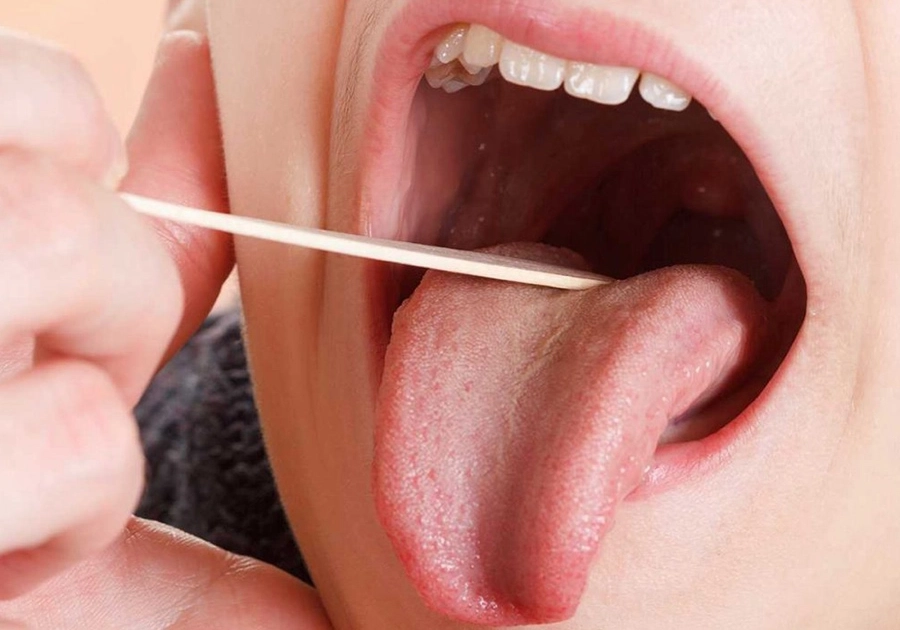
Many people experience characteristic, but usually temporary, mucosal changes, especially on the tongue, palate, and inside of the cheek.
Read more
These include, for example:
- Aphthous ulcers: Small, uncomfortable sores on the mucous membrane
- Fungal infection of the oral mucosa (e.g., thrush): Whitish coating, often with burning
- Herpes simplex: Viral infection including painful blister formation
While such conditions are painful and can interfere with chewing, swallowing, and sometimes even speaking, they can be effectively treated with special mouthwashes, creams, and other medications. In some cases—such as leukoplakia (“white spots”)—careful examination is important to detect any potential malignant development early on.
Read less